Table Of Content

They help break down organic matter and return nutrients back into the ecosystem. One distinguishing feature of an adult housefly is its unique mouthparts that function like a sponge. They cannot bite or chew; instead, they feed by regurgitating digestive juices onto solid food to liquefy it before sucking it up. This feeding habit plays a role in their potential to spread diseases as they often move between filth and human habitats. They prefer decomposing organic material such as food waste or animal feces.
Get Rid Of House Flies And Maggots
Among the pathogens commonly transmitted by house flies are Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Escherichia, Enterococcus, Chlamydia, and many other species that cause illness. Following the egg stage is the larval phase or more commonly known as the maggot stage. This phase lasts approximately five days but can extend up to two weeks if conditions are less than ideal. During this period, larvae undergo rapid growth by feeding voraciously on organic matter in their surroundings.
Human Interactions: Houseflies In Residential Areas, Attraction To Food, Etc
Several methods can help deal with houseflies, including drain treatments and insect sprays. The second molt generally occurs around day three or four of the larval stage, giving rise to third instar larvae. These are significantly larger than both previous stages and can measure up to half an inch in length.
Wild Side: On the house fly - Martha's Vineyard Times
Wild Side: On the house fly.
Posted: Wed, 22 Feb 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Sticky traps
They feed voraciously on the decaying matter around them and go through three instars or molts before moving onto the next stage. If your pet uses a litter box or indoor area for a toilet, clean the area often. If you have a house fly problem in your home, take solace—there are many ways to eliminate the pesky critters. The good news is that you can get rid of house flies with items you probably already have lying around your home. House fly puparia, each with a hole from which a single wasp emerged after feeding on the pupa.
These bacteria can contaminate food or water when flies land on them, presenting a significant risk, particularly in areas with poor sanitation. Spiders also play an essential role in controlling housefly populations by trapping them in their webs. Houseflies often fall prey to different species of spiders, including orb weavers and jumping spiders.
Environmental Impacts: How Temperature, Humidity, And Other Factors Affect The Lifecycle
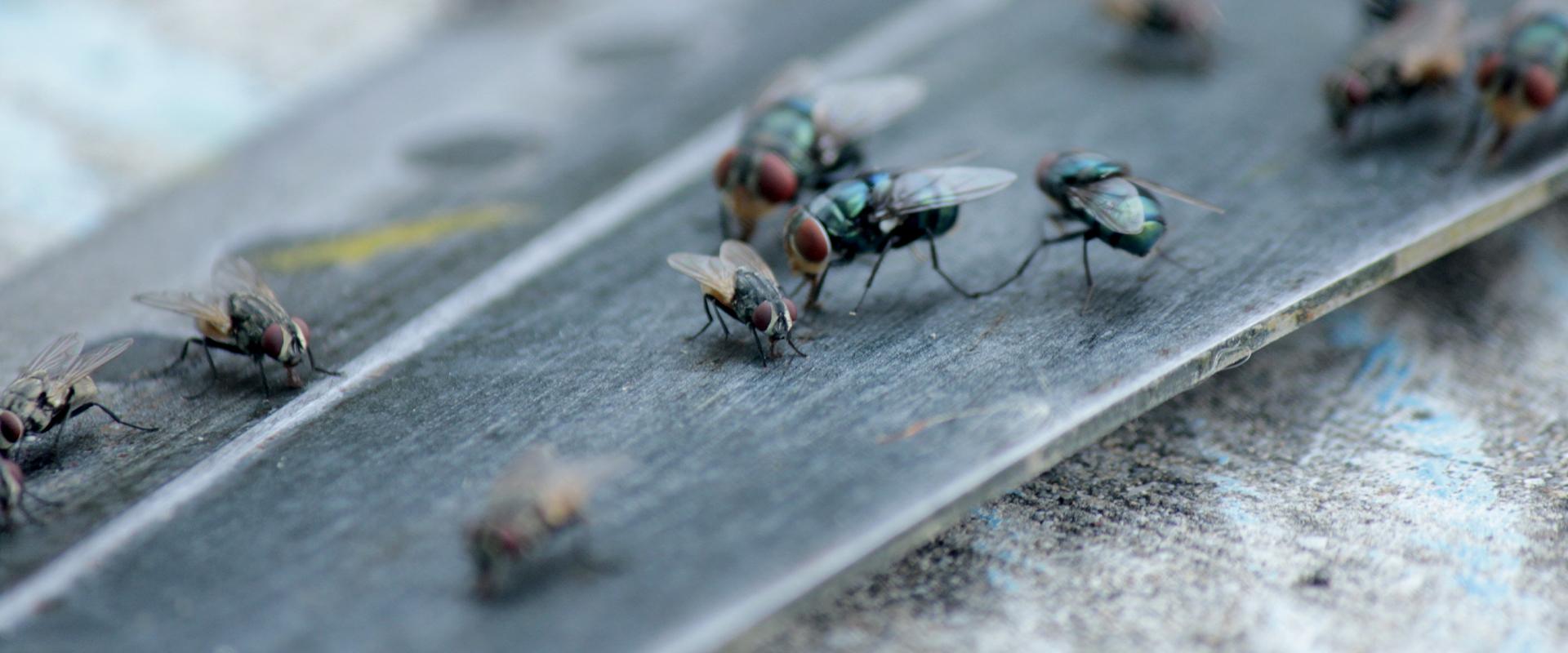

It is an essential part of their diet, as flies cannot live more than 48 hours without access to water. When you are ready to contact a pest control professional, you can find one with the helpful zip code search below. The culmination of these rituals is copulation if all goes well for our persistent male suitor. Traps can be baited with molasses, sugar, fruit or meat, and often are used in combination with a device that captures the attracted flies. The sex pheromone (Z)-9-tricosene also functions as an aggregation pheromone, and is called muscalure. Muscalure is formulated with sugar as a commercially-available fly bait for local population suppression, as well as an enhancement for population monitoring.
Visual representation is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance our understanding of complex processes, such as the life cycle of a housefly. It provides a clear and concise overview of the process, allowing us to visualize each stage and understand how they are interconnected. Once metamorphosis is complete, an adult fly emerges from the puparium. Adult houseflies live for about two to four weeks, during which they mate and continue the cycle. If you’re having a persistent fly problem that won’t go away, chemical-based solutions can be a fast way to get rid of house flies. If your home has been invaded by house flies, this guide will help you eliminate them and prevent more flies from swarming in.
This is where metamorphosis occurs – inside these protective shells, maggots transform into adult flies over several days. To begin with, imagine an oval-shaped diagram divided into four distinct sections, each representing a stage in the life cycle of a housefly – egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Reaching the adult stage is a significant milestone in the life cycle of a housefly. This is when the fly, now fully developed, emerges from its pupal case and takes on the world with newfound abilities and characteristics. In the fascinating journey of a housefly’s life, the pupa stage holds a pivotal position. This is where the most dramatic transformation occurs – an impressive metamorphosis that sees a wriggling larva transform into a buzzing adult fly.
Larva Stage: Insights Into The Larval Phase (Often Called Maggots)

It’s during this period that maggots encase themselves in a protective shell and metamorphose into adult flies. This transformation takes around four to six days under optimal conditions but can stretch out to two weeks when temperatures are cooler. During this phase, which typically lasts from three days to two weeks, depending on environmental conditions, the larval body undergoes significant changes. It breaks down and reorganizes into an adult fly through a process known as histolysis and histogenesis, respectively. In simpler terms, old tissues dissolve while new ones are formed.
Females can lay up to 150 eggs at once and may produce five to six batches throughout their lifetime. A single female housefly can potentially be responsible for over 1 million offspring in her short lifespan if all her descendants survived. The house fly has a complete metamorphosis with distinct egg, larval or maggot, pupal and adult stages.
Fruit and vegetable cull piles, partially incinerated garbage, and incompletely composted manure also are highly favored sites for breeding. In addition to natural ways to get rid of houseflies, you can use insecticides and traps to kill or remove the flies. The emergence of an adult housefly from its pupal case is truly a spectacle to behold!
As carriers of over 100 pathogens, including salmonella and E.coli, due to their feeding habits and breeding grounds in waste materials, they pose a serious risk to public health. Food and materials on which the flies can lay eggs must be removed, destroyed as a breeding medium, or isolated from the egg-laying adult. Since the house fly can complete its life cycle in as little as seven days, removal of wet manure at least twice a week is necessary to break the breeding cycle. Since straw is one of the best fly breeding materials, it is not recommended as bedding. Ordinarily, fly control from 1 to 2 km around a municipality prevents house fly infestations.
More commonly, insecticides (especially insect growth regulators) can be fed to livestock, and residual insecticide in the manure inhibits fly breeding. In animal facilities, insecticides are often applied to the favored resting places of adults, or bait stations established to poison adults with either solid or liquid formulations. Continuous exposure of flies to insecticides has led to development of insecticide resistance to many insecticides. Of particular concern is the movement of flies from animal or human feces to food that will be eaten uncooked by humans. Also, when consumed by flies, some pathogens can be harbored in the mouthparts or alimentary canal for several days, and then be transmitted when flies defecate or regurgitate. In situations where plumbing is lacking, such as open latrines, serious health problems can develop, especially if there are outdoor food markets, hospitals, or slaughter houses nearby.